Schottky Diode
Schottky Diode
In this type of diode, the junction is formed by contacting the semiconductor material with metal. Due to this, the forward voltage drop is decreased to a minimum. The semiconductor material is N-type silicon, which acts as an anode and metals such as Chromium, Platinum, Tungsten etc. act as cathodes.
Due to the metal junction, these diodes have high current conducting capability and hence the switching time is reduced. So, Schottky Diode has greater use in switching applications. Mainly because of the metal-semiconductor junction, the voltage drop is low, which in turn increases the diode performance and reduces power loss. So, these are used in high-frequency rectifier applications. The symbol of the Schottky diode is shown below.
The Schottky diode is a type of metal-semiconductor junction diode, which is also known as a hot-carrier diode, low-voltage diode or Schottky barrier diode. The Schottky diode is formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. Schottky diode offers fast switching action and has a low forward voltage drop. As we are aware that in a PN junction diode, p-type and n-type are joined together to form a PN junction. Whereas, in a Schottky diode metals like platinum or aluminum are used instead of P-type semiconductors.
The symbol for the Schottky barrier diode is based around the basic diode circuit symbol. The circuit symbol of the Schottky diode is shown in the figure.
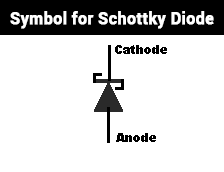
Schottky Diode Symbol
V-I Characteristics of Schottky Diode
The V-I characteristics of Schottky diodes are very much similar to the PN junction diode. Current is the dependent variable while voltage is the independent variable in the Schottky diode. The forward voltage drop of the Schottky diode is low between 0.2 to 0.3 volts.

Working of a Schottky Diode
- The operation relies on the principle that the electrons in different materials have different potential energy.
- N-type semiconductors have higher potential energy than electrons of metals.
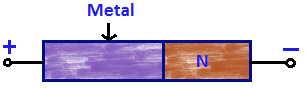
- When these two are brought into contact, there is a flow of electrons in both directions across the metal-semiconductor interface.
- A voltage is applied to the Schottky so that the metal is positive when compared to the semiconductor.
- The voltage opposes the built-in potential and makes the current flow easy.
Applications of Schottky Diode

Schottky diodes have been useful for the industry of electronics that has spotted many applications in diode rectifiers because of its unique properties. Here are some major areas where it is widely used.
RF mixer and detector diode:
The Schottky diode consists of its radio frequency functions owing to its switching speed at the highest level and top frequency capability. The Schottky barrier diodes come in handy for diode ring mixers with high performance.
Power rectifier:
The Schottky barrier diodes also have functions with high power as rectifiers. The high density of current and voltage drop with low forward shows that the wastage of power is lesser than the normal PN junction diodes.
Power OR circuits:
This diode would be useful for functions where two different power supplies drive a load like in a battery supply. It is important that the power coming from the supply should not mix with the others.
Solar Cell Applications:
As we know, solar cells are usually linked to the batteries that are rechargeable, mostly batteries with lead acid since a power supply must be necessary round the clock. Solar cells would not support the applied charge in reverse and thus, a diode would be used in a proportional pattern of the solar cells.
Advantages of Schottky diode
The following are the advantages of the Schottky diode:
- The capacitance of the diode is low as the depletion region of the diode is negligible.
- The reverse recovery time of the diode is very fast, that is the change from ON to OFF state is fast.
- The current density of the diode is high as the depletion region is negligible.
- The turn-on voltage of the diode is 0.2 to 0.3 volts, which is very low.
Disadvantages of Schottky diode
The only disadvantage of Schottky diodes is that the reverse saturation current of the diode is large.
What is the difference between the Schottky diode and the PN junction diode?
| Schottky diode | PN junction diode |
| In this diode, the junction is formed between the n-type semiconductor and the metal plate | In this diode, the junction is formed between the p-type and n-type semiconductors |
| The forward voltage drop is low | The forward voltage drop for the PN junction diode is more |
| Reverse recovery loss and reverse recovery time are very less | Reverse recovery loss and reverse recovery time are more |
| It is a unipolar device | It is a bipolar device |
| The conduction of current happens only due to the movement of electrons | The conduction of current happens due to the movement of electrons and holes |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Why is there no reverse recovery time in the diode?
There are no stored charges as the metal-semiconductor junction is used, due to which the switching is faster.

Comments
Post a Comment